Blood Clots In Men
Blood clot, the silent killer, is becoming a threat with each passing day. Most men over 40 years of age carry these little dangerous solid balls of blood in their veins. These blood clots cause intense pain and in more serious cases, they can even prove to be fatal.
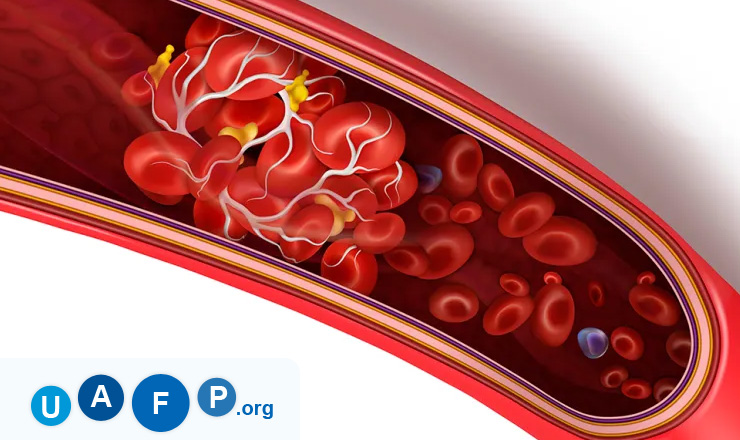
Blood Clots: Life Savers Or Danger?
Formation of blood clot, in general is a life saving phenomenon. When we get a bruise or a cut and blood oozes out, in no time, it coagulates and forms a clot that seals the wound. Hence, clotting of blood is an essential process that saves blood loss. So, why are these blood clots dangerous?
The danger lies in the fact that sometimes these blood clots work against our bodies. This happens when blood clots form in veins, blocking them and restricting the normal blood flow. These clots most commonly form in deep veins. The blood thickens and forms a thrombus (clump) and blocks the veins. This condition is called as DVT, i.e., Deep Vein Thrombosis. Apart from the deep veins of legs, these clots can also form in the vessels of arms and pelvis. They may stay at one place or move to narrower vessels and vital parts like heart, brain, lungs, etc. They can also lead to deaths.
The Common Causes And Risk Factors Of Blood Clots
There are many factors that are associated with the formation of blood clots in men. The major causes and risk factors of blood clot formation are:
- Prolonged Inactivity: Prolonged immobility is the commonest cause and risk factor of developing blood clots. If a man is bed ridden since a long period of time as a result of grave illness or due to any other reason, he is at a higher risk of developing blood clots.
- Trauma: Any history of recent trauma, e.g., hip or leg fracture is a common cause and risk factor of blood clot formation.
- Surgery: Recent orthopaedic, cardiac or any other surgery increases the chance of blood clot.
- Genetics: Genes are directly related to blood clot formation. Blood clotting disorders are acquired genetically.
- Any damage to blood vessel may cause clot formation.
- Change in the normal blood flow may lead to blood clot formation.
- Heart attack increases the susceptibility of clot formation.
- Obesity increases the risk of blood clot formation.
- Cancer is also a common risk factor.
Symptoms Of Blood Clots
The symptoms of blood clots vary according to the location.- Atrial Fibrillation: No symptom
- Brain: Symptoms of stroke
- DVT in leg or arm: Swelling, discoloration or redness, pain and warmth
- In the artery supplying bowel: Bloody bowel movements and pain in abdomen
- In coronary artery: Signs and symptoms of heart attack
- In cerebral artery: Signs and symptoms of stroke
- Arterial clot in arm or leg: Cool, painful and pulse less extremity.
Early Stage Blood Clot Symptoms
Blood clots can occur in different parts of the body and present various symptoms depending on their location. Early stage blood clot symptoms may not always be obvious or can be mistaken for other conditions. It's crucial to be aware of potential signs and seek medical attention if you suspect a blood clot. Here are some common early stage symptoms:
- Swelling: Unexplained swelling in the arms, legs, or other parts of the body might be a sign of a blood clot blocking blood flow.
- Pain or tenderness: You may experience pain or tenderness in the affected area. For example, if it's a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the leg, you might feel pain or cramping in the calf or thigh.
- Warmth and redness: The skin around the clot might feel warmer than usual and appear red or discolored.
- Visible veins: In some cases, the veins near the clot may become more visible or engorged.
- Shortness of breath: If the blood clot travels to the lungs (pulmonary embolism), it can cause sudden and severe shortness of breath, chest pain, and sometimes coughing up blood. This is a medical emergency.
- Rapid heart rate: A blood clot in the lungs may lead to an increased heart rate.
- Dizziness or fainting: A pulmonary embolism can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting.
It is essential to note that some blood clots may not present any symptoms, making them even more dangerous as they can go unnoticed until they cause severe complications. Certain factors increase the risk of blood clots, such as a family history of clotting disorders, prolonged immobility (e.g., after surgery or during long flights), smoking, obesity, and certain medical conditions.
Diagnosis Of Blood Clots
Blood clots are diagnosed by:
- MRI
- CT Scan
- Venography
- Ultrasound
Treatment Of Blood Clots
- Medications
Though blood clots can’t be removed by medications, but they at least help in arresting their growth and further formation of new clots. Anticoagulants are given to control blood clots.
Clot-busting drugs are used in case of large clot formation, but these medications are rarely used.
- Compression Stockings
Compression stockings help to control pain.
How To Dissolve Blood Clots Naturally
However, there are some lifestyle changes and natural approaches that can help reduce the risk of blood clots or support overall cardiovascular health. Here are some general guidelines:
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve blood circulation and lower the risk of blood clots. Activities like walking, swimming, or biking can be beneficial.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reducing intake of processed foods, saturated fats, and excess salt can also help.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated can assist in preventing blood from thickening and clotting excessively. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Avoid prolonged immobility: If you have a sedentary lifestyle or spend long periods sitting (e.g., during long flights or car rides), make sure to move your legs and stretch regularly.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation and an increased risk of blood clots. Find relaxation techniques that work for you, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna) or flaxseeds, may help improve heart health.
- Garlic: Some studies suggest that garlic may have anticoagulant properties and help prevent blood clots. However, consult your doctor before incorporating garlic supplements or large amounts of garlic into your diet, especially if you are on other medications, as it may interact with certain drugs.
- Turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin, which has potential anticoagulant effects. It may help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of clots. Again, consult your doctor before using turmeric supplements, especially if you have a bleeding disorder or are taking blood-thinning medications.




