Everything to Know About Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is a form of skin condition where the skin of an individual turns thicker than it is usually seen in certain parts of the body. Keratin is the name given for the fibrous, tough protein present in the skin, fingernails, and hair. When there is an incidence of inflammation, the body is likely to produce keratin in excess, as a response to pressure or a genetic condition.
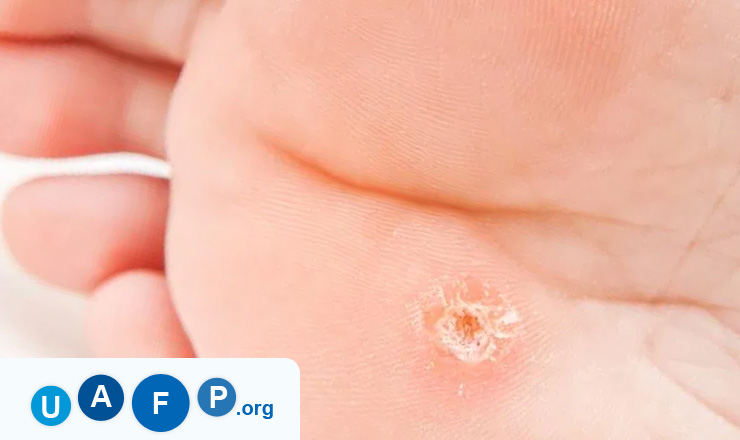
Most of the variations of Hyperkeratosis can be treated using preventive measures along with medications. Hyperkeratosis is majorly divided into two types. Psoriasis and eczema are two forms of this condition.
Types and Causes
Hyperkeratosis could result from pressure, irritation, or inflammation to the skin. This type is called pressure-related hyperkeratosis. In the incidence of pressure, the skin will try to produce extra keratin layers for protecting the areas of skin that has been damaged.
On parts of the skin that has not been irritated, non-pressure Hyperkeratosis develops. This type could occur because of a genetic predisposition.
Other types include:
- Warts
- Psoriasis
- Planter warts
- Linchen planus (white patches growing inside the person's mouth)
- Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (inherited skin disorder)
- Eczema
- Corns
- Calluses
- Actinic keratosis (resulting from excessive skin exposure)
If there is a presence of Hyperkeratosis on the skin, it is best to contact a doctor regarding it.
Symptoms
There can be several forms of symptoms associated to Hyperkeratosis. Most of the symptoms include a patchy or rough skin that is different from the skin adjacent to it.
The symptoms commonly seen in some of the types of Hyperkeratosis are:
- Corns: Lesion can be seen between or on the toes. The corn contains a centre lesion made of very hard keratin along with an outer ring made of hard tissue, slightly softer than the centre.
- Calluses: The affected area has a thickened skin, mostly seen near the feet, but can appear on fingers as well. The thickness is even is this type of Hyperkeratosis.
- Eczema: The skin is itchy, red, and may also have small bumps or patches.
- Plague psoriasis: The skin cells have excess build-up which appears to be scaled and silvery.
Treatment Options
The form of Hyperkeratosis the person has will dictate the treatment method. Medical as well as home treatments are available for Hyperkeratosis.
To avoid Hyperkeratosis, here are some ways that can be suggested:
- Avoid stimuli that triggers allergy, like pollen and pet dander which could result in skin inflammation.
- Avoid going out barefoot in areas that are known to be prone to fungi, like pools, gyms, and locker rooms.
- Wear shoes that are well-fitting and comfortable in nature. Go outside in the sun after putting on sun-screen that at least has an SPF of 30. You can also make use of protective clothing like long sleeves or hat.
Doctors prescribe medications, like corticosteroid creams when a person is suffering from lichen planus or eczema.
If the Hyperkeratosis causes a lot of discomfort or pain, he/she must get it check from a doctor. An Occurrence of the severe symptoms also calls for medical attention.




